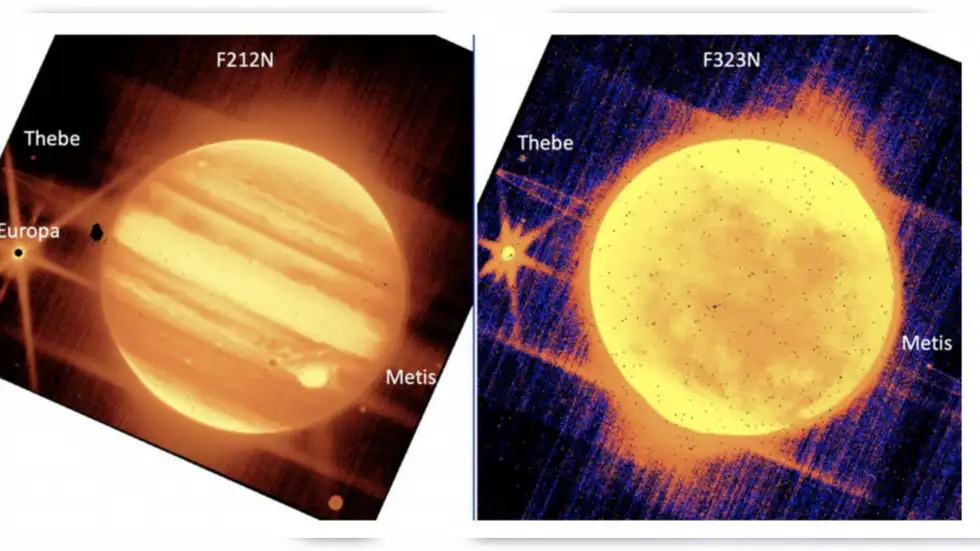
The James Webb telescope of NASA has taken stunning photos of nebulae, groups of galaxies and even the “deepest” view of the universe. It has also taken photos of Jupiter to see if it can be used to observe nearby celestial objects like moons and asteroids, as well other elements like planet rings and satellites.
NASA said, “Fans of Jupiter will recognize some familiar features of our solar system’s enormous planet in these images seen through Webb’s infrared gaze. A view from the NIRCam instrument’s short-wavelength filter shows distinct bands that encircle the planet as well as the Great Red Spot, a storm big enough to swallow the Earth. The iconic spot appears white in this image because of the way Webb’s infrared image was processed.”
Bryan Holler, a scientist at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, who helped plan these observations said, “Combined with the deep field images released the other day, these images of Jupiter demonstrate the full grasp of what Webb can observe, from the faintest, most distant observable galaxies to planets in our own cosmic backyard that you can see with the naked eye from your actual backyard,”.
According to Engadget, “It’s worth noting that James Webb captured these images moving across its field of view in three separate observations, proving that it’s capable of finding and tracking stars in the vicinity of a celestial body as bright as Jupiter. That means it can be used to study moons in our solar system and could give us the first images of the plumes of material known to spew out of natural satellites like Europa and Saturn’s moon Enceladus.” They also said, “The team also tracked asteroids in the asteroid belt to figure out the fastest objects it can observe. They found that it can still get gather data from objects moving up to 67 milliarcseconds per second across its field of view. NASA says that’s equivalent to tracking a turtle moving from a mile away. As Stefanie Milam, James Webb’s deputy project scientist, said, these images show that “everything worked brilliantly.” We can expect not just more impressively detailed images of space in the future, but also information that could shed more light on how the first galaxies had formed.”